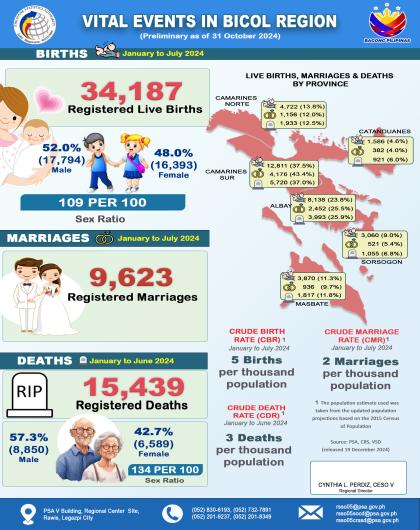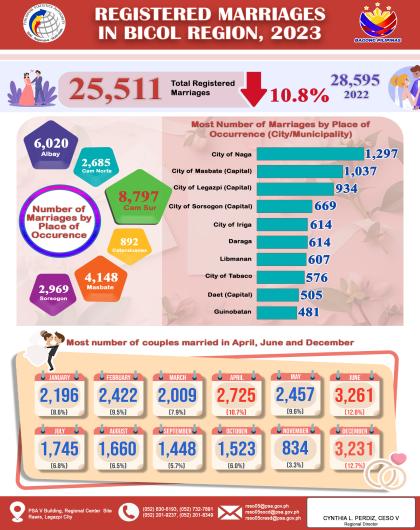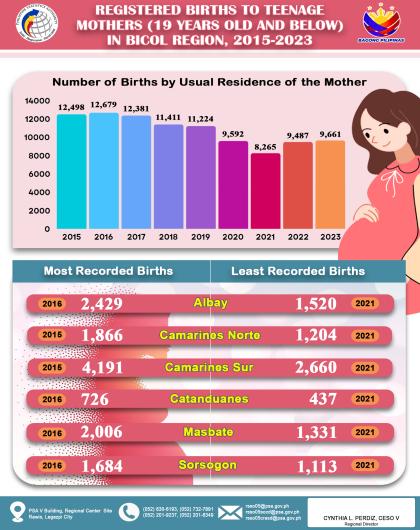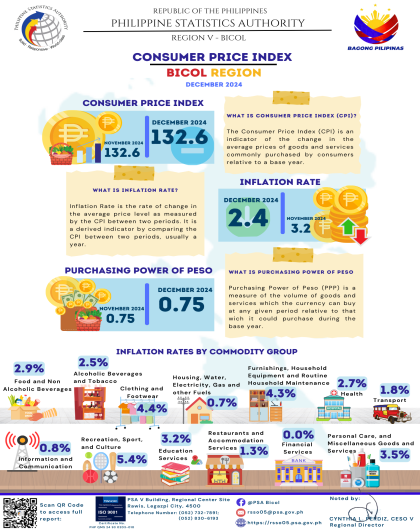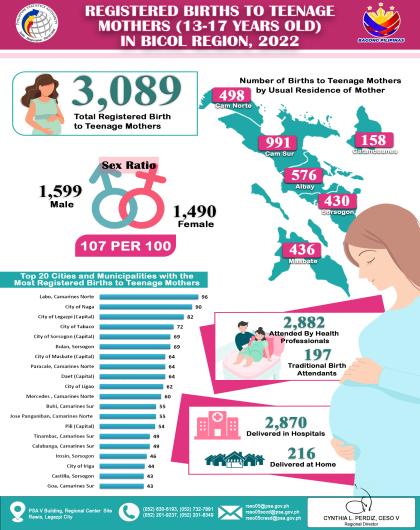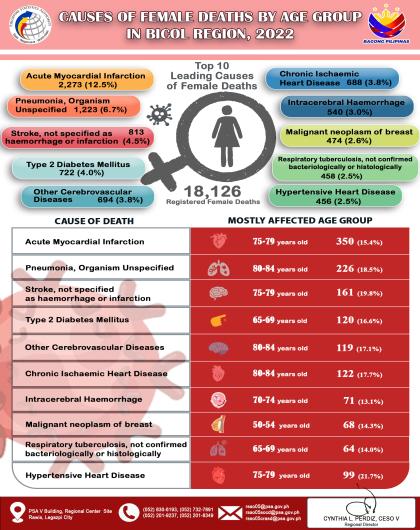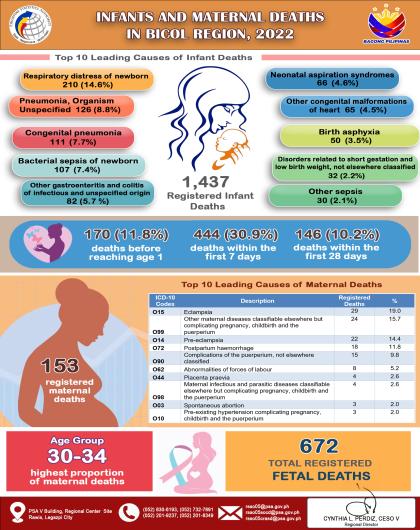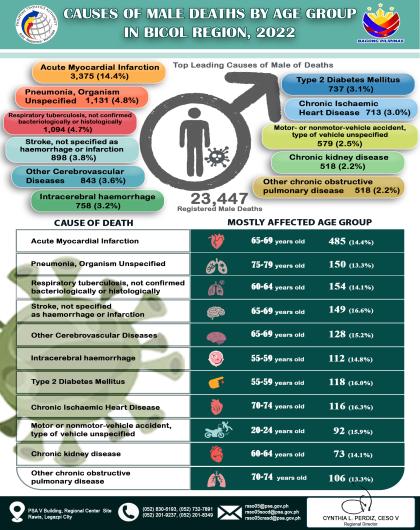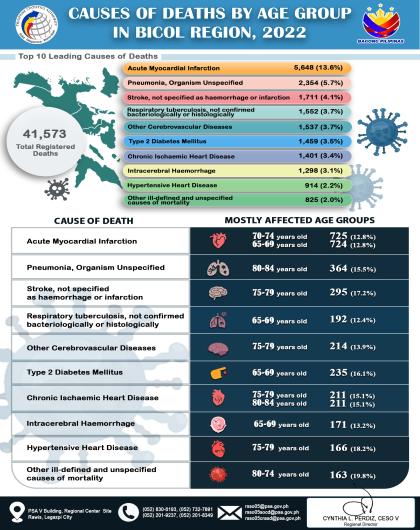
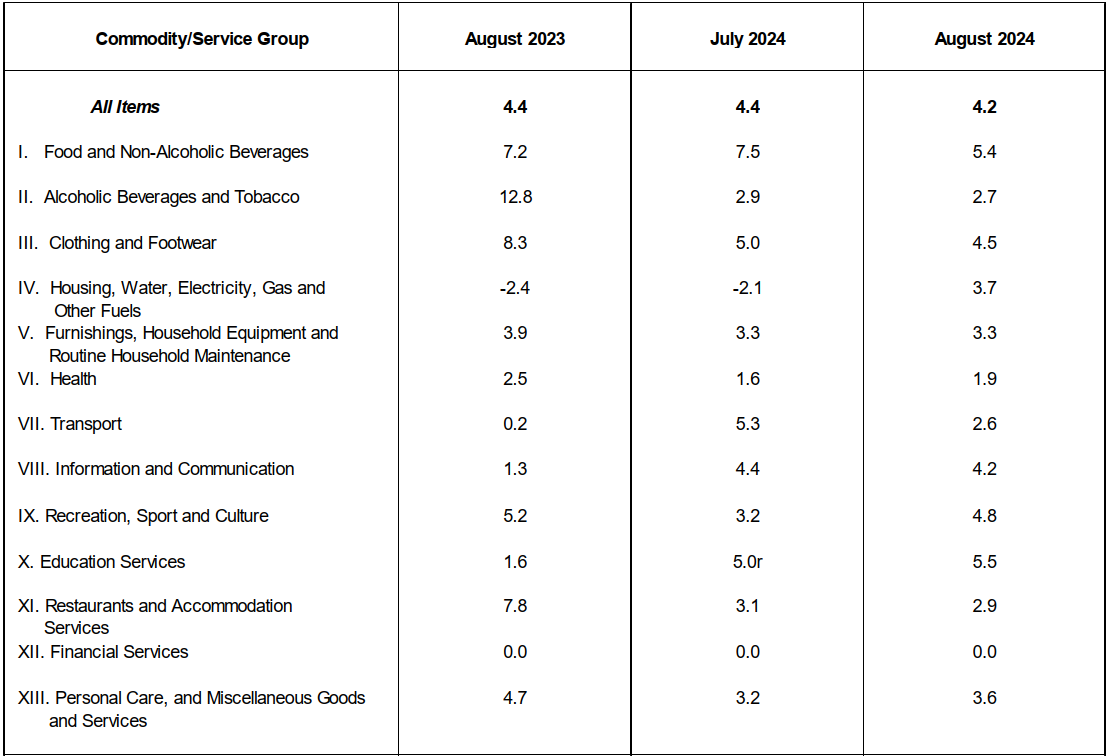
Headline Inflation
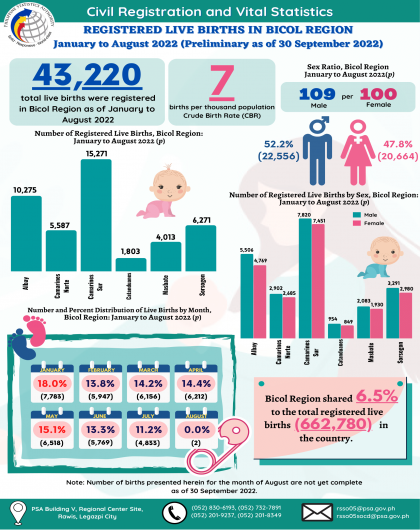
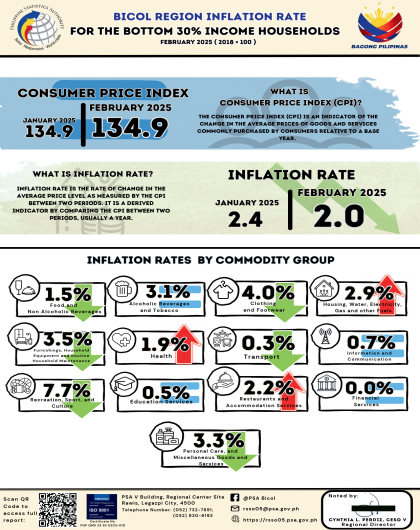
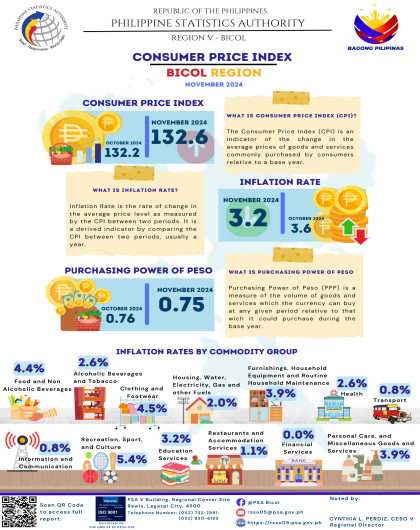
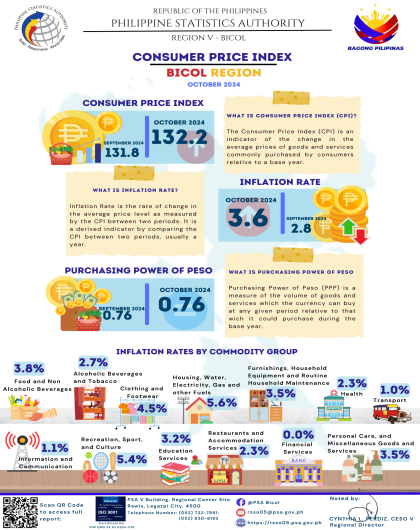
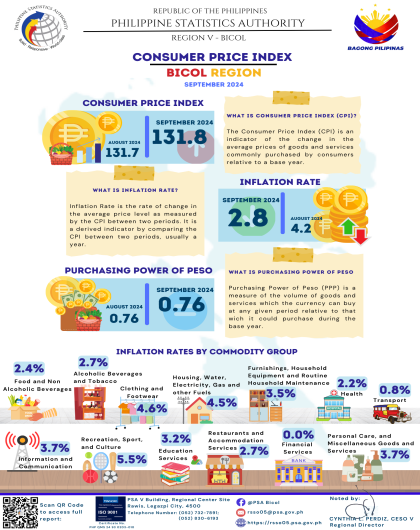
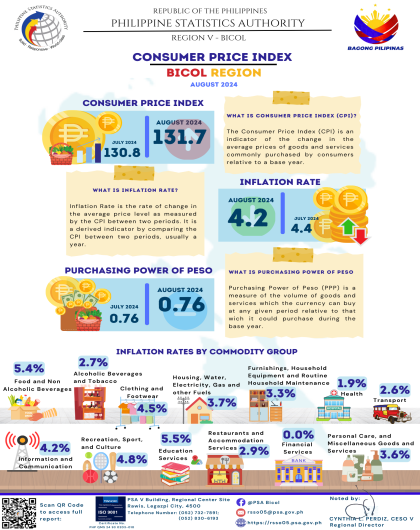
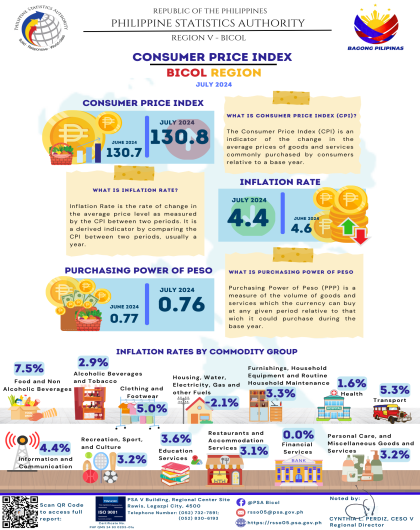
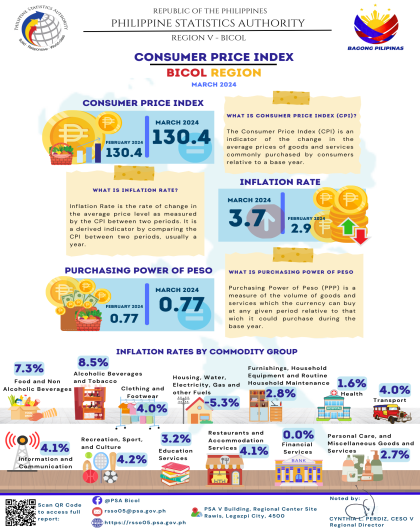
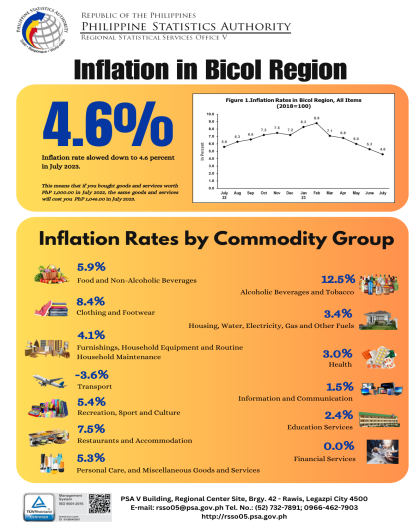
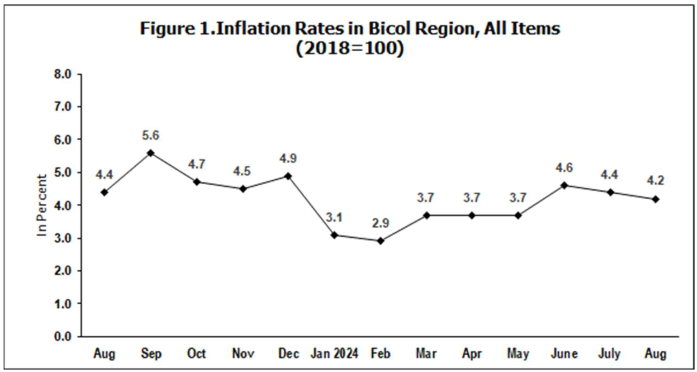
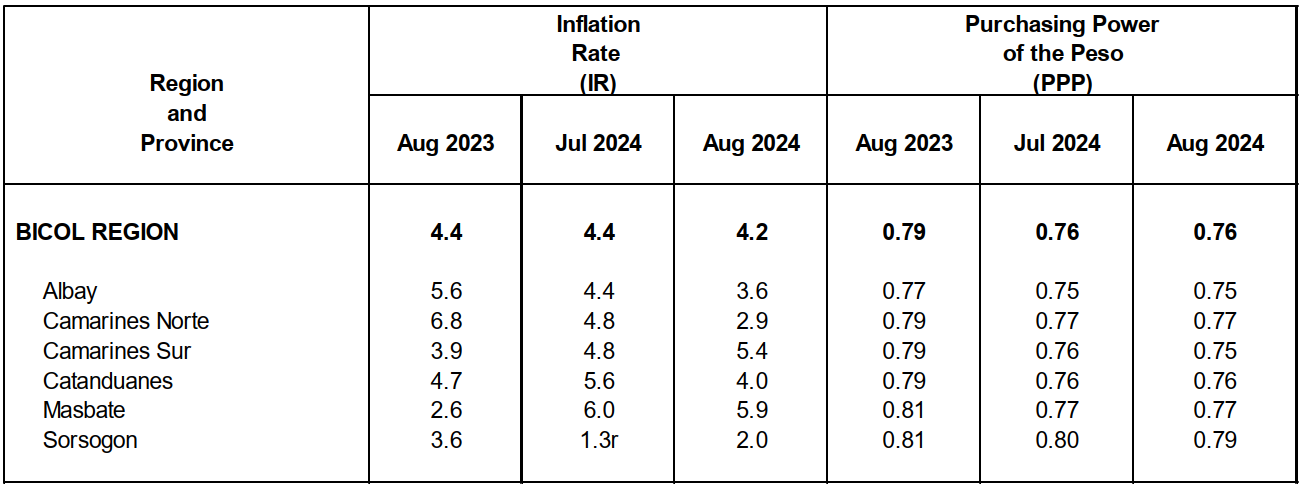
The region’s headline inflation or overall inflation eased to 4.2 percent in August 2024 from 4.4 percent in July 2024. This brings the regional average inflation from January to August 2024 to 3.8 percent. In August 2023, the inflation rate was recorded at 4.4 percent.
Main Drivers to the Downward Trend of the Headline Inflation
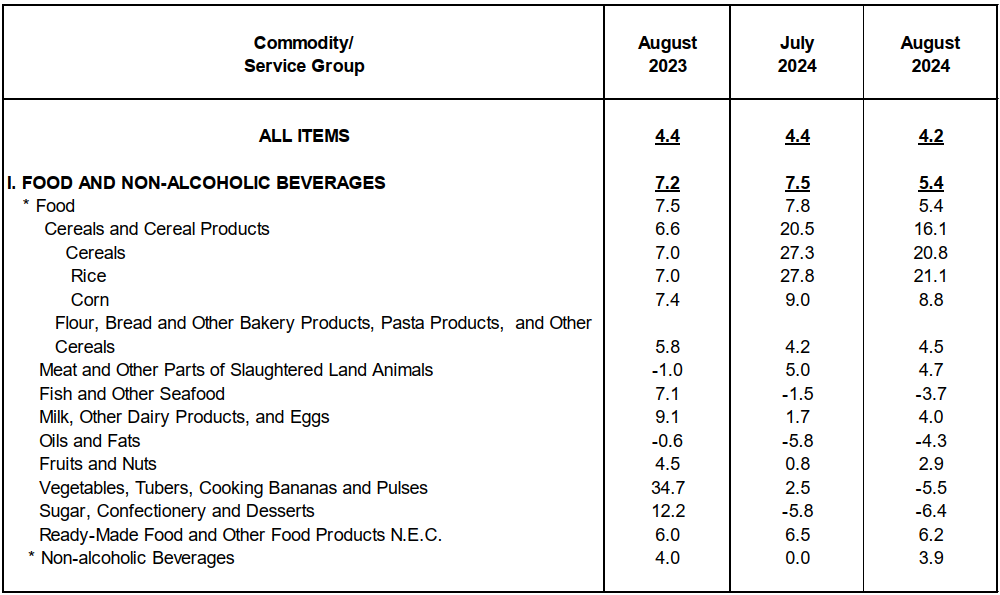
The downtrend in the overall inflation in August 2024 was primarily brought about by the slower annual increment of food and non-alcoholic beverages at 5.4 percent in August 2024 from 7.5 percent in the previous month. Also contributing to the downtrend was transport with a slower annual increase of 2.6 percent during the month from 5.3 percent annual increase in July 2024.
Lower annual increments were also noted in the indices of the following commodity groups during the month:
a. Alcoholic beverages and tobacco, 2.7 percent from 2.9 percent;
b. Clothing and footwear, 4.5 percent from 5.0 percent;
c. Information and communication, 4.2 percent from 4.4 percent; and
d. Restaurants and accommodation services, 2.9 percent from 3.1 percent.
In contrast, the following commodity groups registered higher inflation rates during the
month:
a. Housing, water, electricity, gas and other fuels, 3.7 percent from -2.1 percent;
b. Health, 1.9 percent from 1.6 percent;
c. Recreation, sport and culture, 4.8 percent from 3.2 percent;
d. Education services, 5.5 percent from 5.0 percent; and
e. Personal care, and miscellaneous goods and services, 3.6 percent from 3.2 percent.
The indices of the rest of the commodity groups retained their respective previous month’s annual rates.
Main Contributors to the Headline Inflation
The top three commodity groups contributing to the August 2024 overall inflation were the following:
a. Food and non-alcoholic beverages with 57.0 percent share or 2.4 percentage points;
b. Housing, water, electricity, gas and other fuels with 15.8 percent share or 0.7 percentage point; and
c. Transport with 4.4 percent share or 0.2 percentage point.
Food Inflation
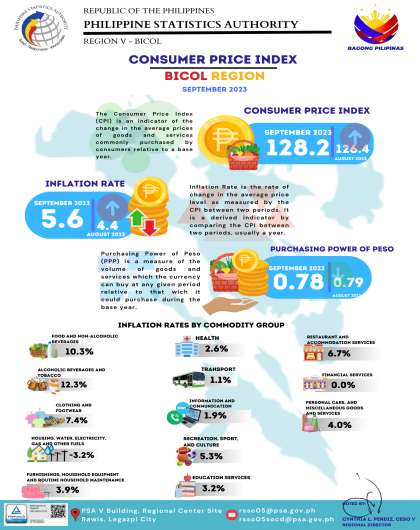
Food inflation at the regional level eased to 5.4 percent in August 2024 from 7.8 percent in
the previous month. In August 2023, food inflation was higher at 7.5 percent.
Main Drivers to the Downward Trend of Food Inflation
The deceleration of food inflation in August 2024 was primarily brought about by the slower inflation rate of rice with 21.1 percent in August 2024 from 27.8 percent in the previous month. This was followed by vegetables, tubers, plantains, cooking bananas and pulses with a year-on-year decline of 5.5 percent during the month from 2.5 percent annual increase in July 2024.
In addition, faster annual declines were noted in the indices of fish and other seafood at 3.7 percent and sugar, confectionery and desserts at 6.4 percent during the month from their respective annual decreases of 1.5 percent and 5.8 percent in the previous month. Slower annual decline was observed in the index of oils and fats at 4.3 percent.
Moreover, lower inflation rates during the month were noted in the following food groups:
a. Corn, 8.8 percent from 9.0 percent;
b. Meat and other parts of slaughtered land animals, 4.7 percent from 5.0 percent; and
c. Ready-made food and other food products not elsewhere classified, 6.2 percent from 6.5 percent.
In contrast, the following commodity groups registered higher inflation rates during the month:
a. Flour, bread and other bakery products, pasta products, and other cereals, 4.5 percent from 4.2 percent;
b. Milk, other dairy products and eggs, 4.0 percent from 1.7 percent; and
c. Fruits and nuts, 2.9 percent from 0.8 percent.
Main contributors to the Food Inflation
Food inflation shared 54.3 percent or 2.3 percentage points to the overall inflation in August 2024. The top three food groups in terms of contribution to the food inflation during the month were the following:
a. Cereals and cereal products, which includes rice, corn, flour, bread and other bakery products, pasta products, and other cereals, with a share of 96.2percent or 5.2 percentage points;
b. Meat and other parts of slaughtered land animals with a share of 12.1 percent or 0.7 percentage point; and
c. Milk, other dairy products and eggs with a share of 5.3 percent or 0.3 percentage point.
DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS
Consumer Price Index - a statistical measure of the change in average retail prices of a fixed basket of goods and services bought by a specific group of consumers in a given area in a given period of time.
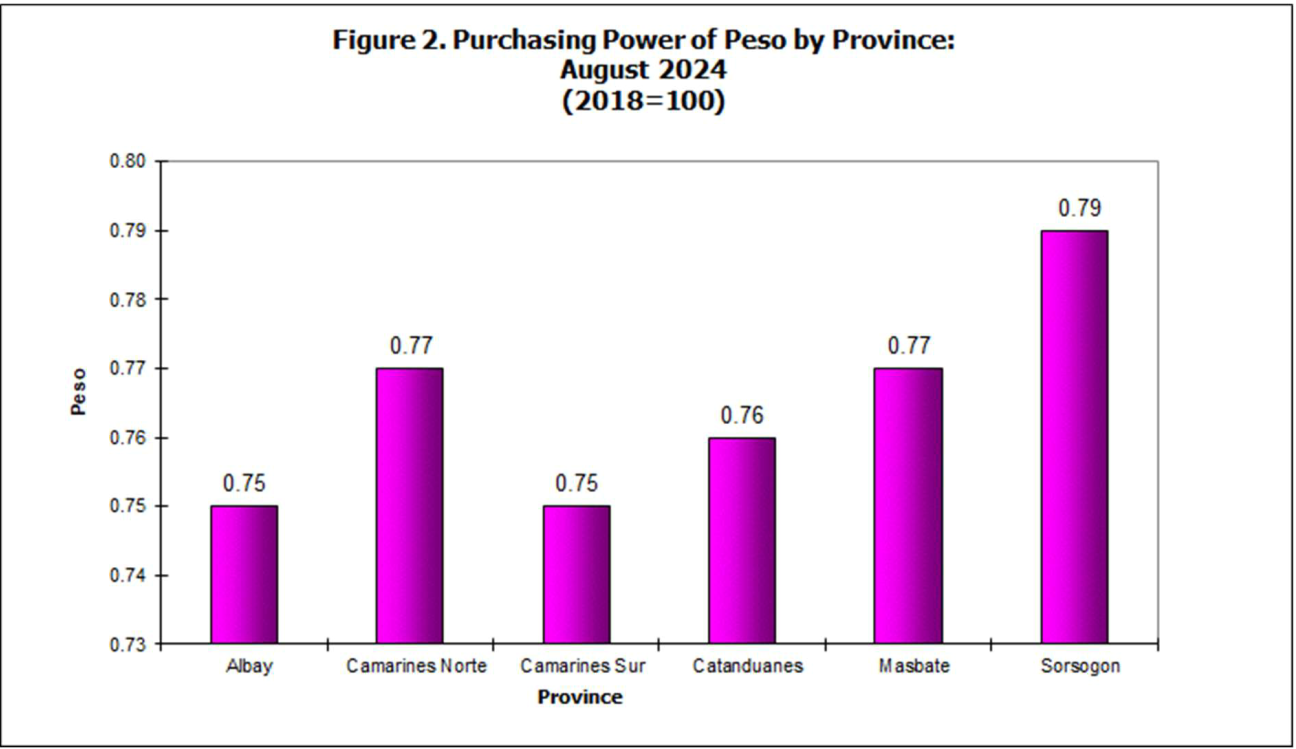
Purchasing Power of the Currency or Peso (PPP) - a measure of the volume of goods and services which the currency can buy at any given period relative to that which it could purchase during the base year. It is computed as the reciprocal of the CPI for the period under review multiplied by 100.
Market Basket - the total number of goods and services in constant amounts and qualities which are samples of the goods and services available in the market and included in the construction of the index. CPI market basket was selected to represent the composite price behavior of all goods and services purchased by consumers. Composition of the 2012 market basket was determined based on the results of the 2018 update of the 2012 basket. Provinces and selected cities had own market baskets.
Base Year - it identifies the base period with which the index relates. It is a period of time chosen as reference on which a price index is computed. The index for the base year is 100.
Retail Price - the actual price at which retailers sell a commodity on spot or earliest delivery, usually in small quantities for consumption and not for resale. It is confined to transactions on cash basis in the free market and excludes black-market prices and prices of commodities that are on sale as in summer sales, anniversary sales, Christmas sales, etc.
Percent Change - the percent point change expressed as percent of the index of the earliest date.
Inflation Rate - the annual rate of change or the year-on-year change of the CPI. Inflation is interpreted in terms of declining purchasing power of money.
Note to Users:
The monthly Consumer Price Index is computed based on the average retail prices of goods and services collected during the first week and mid-month of the reference month.